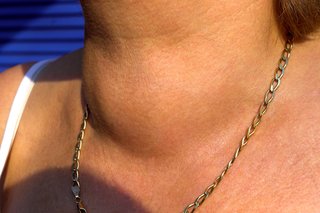
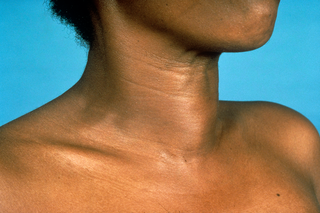
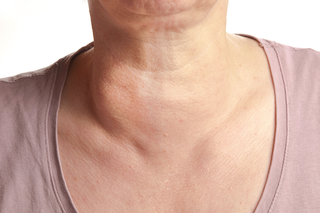
A goitre is a lump or swelling at the front of the neck caused by a swollen thyroid. The thyroid is a small gland in your neck that makes hormones. Goitres are not usually serious but should be checked by a GP.
Check if you have a goitre
The main symptom of a goitre is a swelling at the front of the neck, which is usually painless.
You may also have other symptoms including:
- a cough that does not go away
- a hoarse voice or voice changes
- feeling like something is stuck in your throat
- a wheezing noise when you breathe
- finding it hard to swallow or breathe
Non-urgent advice: See a GP if:
- you think you have a goitre
It's not usually serious, but it's best to get it checked.
Immediate action required: Call 999 or go to A&E if:
- you're finding it hard to breathe
Do not drive to A&E. Ask someone to drive you or call 999 and ask for an ambulance.
Bring any medicines you take with you.
Treatments for a goitre
Most goitres are small and do not cause any problems. Sometimes they do not need treatment.
You will usually need tests like blood tests and sometimes an ultrasound scan to find out what is causing your goitre.
If it is caused by a health condition like an underactive or overactive thyroid, it can usually be treated with medicines.
If your goitre is making breathing and swallowing difficult, you may have surgery to remove some or all of your thyroid.
Causes of a goitre
A goitre happens when your thyroid gland is swollen.
Some reasons why your thyroid might be swollen include:
- an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism)
- an underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism)
- harmless lumps (nodules) on the thyroid
- hormone changes during puberty, pregnancy or the menopause
- an inflamed thyroid gland (thyroiditis)
- having a condition with your immune system, like Grave's disease
- not enough iodine in your diet - this is rare in the UK
- thyroid cancer – this is rare
Page last reviewed: 27 July 2022
Next review due: 27 July 2025