Check if you have impetigo
Impetigo starts with red sores or blisters, but the redness may be harder to see on brown and black skin.
The sores or blisters quickly burst and often leave crusty, golden-brown patches.
The patches can:
- look a bit like cornflakes stuck to your skin
- get bigger and spread to other parts of your body
- be itchy and are sometimes painful
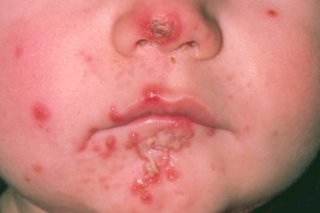
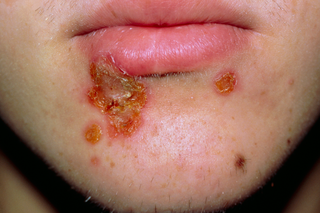
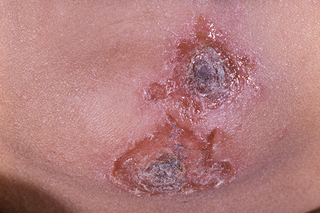
If you're not sure it's impetigo
| Skin symptoms | Possible cause |
|---|---|
|
Blisters on lips or around the mouth |
|
|
Itchy, dry, cracked or sore skin |
|
|
Itchy blisters |
Non-urgent advice: See a GP if you or your child:
- might have impetigo
- has had treatment for impetigo but the symptoms have changed or become worse
- had impetigo before and it keeps coming back
Impetigo is very infectious. Check with the GP before you go into the surgery. They may suggest a phone consultation.
A pharmacist can help with impetigo
You can also speak to a pharmacist if you think you or your child have impetigo. They can provide the same treatment you would get from a GP, if you need it.
Treatment for impetigo
A GP or pharmacist will check if your symptoms are caused by a more serious skin infection, like cellulitis.
If it's impetigo, they can prescribe:
- hydrogen peroxide cream if it's in 1 area
- antibiotic cream or tablets if it's more widespread
- antibiotic tablets if you have bullous impetigo
Babies and people with a weakened immune system may also need antibiotic tablets to stop the infection causing more serious problems.
If your impetigo keeps coming back
A GP can take a swab from your skin to check for the bacteria that causes impetigo. They may also take a swab from inside your nose.
They might prescribe an antiseptic body wash, nasal ointment, or both, to try to clear the bacteria and stop the impetigo coming back.
Important: Make sure you finish treatment
Do not stop taking the antibiotic tablets early, even if the impetigo starts to clear up.
How to stop impetigo spreading or getting worse
Impetigo can be easily spread to other parts of your body or to other people through skin-to-skin contact.
You can also get it by touching things that have been infected, like towels and bedding.
Impetigo stops being contagious:
- 48 hours after you start using hydrogen peroxide cream or antibiotics prescribed by a GP or pharmacist
- when the patches dry out and crust over (if you do not get treatment)
There are some things you can do to help stop impetigo spreading or getting worse while it's still contagious.
Do
-
stay away from work, school or nursery until no longer contagious
-
wash affected areas with soap and water and dry them thoroughly
-
wash your hands frequently, particularly before and after using antibiotic cream
-
wash flannels, towels, sheets and pillowcases at a high temperature
-
wash toys with detergent and warm water if your children have impetigo
Don’t
-
do not touch or scratch sores, blisters or crusty patches – this also helps stop scarring
-
do not have close contact with children or people with diabetes or a weakened immune system (if they're having chemotherapy, for example)
-
do not share flannels, towels, sheets or pillowcases
-
do not prepare food for other people if you have impetigo
-
do not go to the gym or play contact sports like football
How to avoid impetigo
Impetigo usually infects skin that's already damaged.
You can get it if you have a minor injury like a cut, scratch or insect bite, or a skin condition.
To avoid getting impetigo:
Page last reviewed: 06 June 2024
Next review due: 06 June 2027